Power Factor Improvement Methods
Welcome to englogs.com In this article, we will study about the various methods of Power Factor Improvement.
Power Factor plays a very important role in Electric Power Transmission & Distribution. Low Power Factor has many disadvantages associated to it. Normally, the power factor of the generating station should lie between 0.8-0.9. Sometimes, the power factor is lower and in such cases specials equipments are added to achieve higher power factor.
Some Most Commonly used Equipments are :
- Static Capacitor
- Synchronous Condenser
STATIC CAPACITOR:
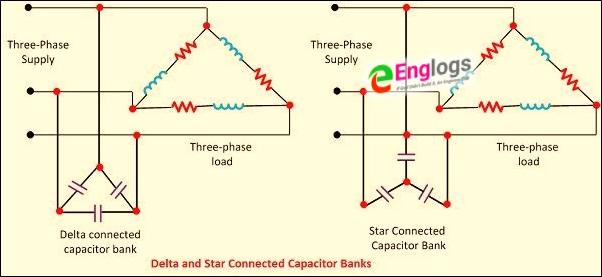
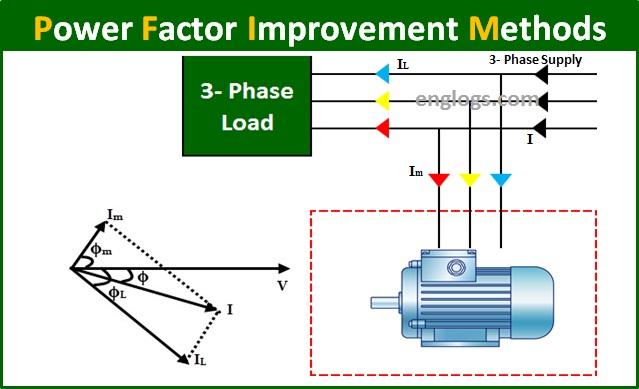
It is well known that capacitor draws a leading current , which means that current in the capacitor leads the voltage across the capacitor. This property of the Capacitor is used in Power Factor Improvement. Generally, the Capacitor of the suitable rating is connected in parallel with the equipment having low power factor. This partly or completely neutralises the lagging current drawn by the equipment. This increases the power factor. For 3-phase loads, the capacitor can be connected in star or delta.
ADVANTAGES:
- This method requires little maintenance as there are no rotating parts.
- Its performance is not affected by the surrounding/atmospheric conditons.
- Installation is easy and does not require any construction work.
- They have low losses.
DISADVANTAGES:
- Have Shorter Life.
- If the voltage exceeds the rated value, then they are easily damaged.
- Once Damaged, their repair is not economical
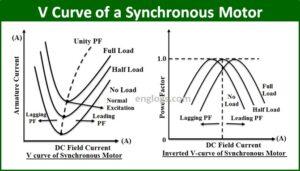
SYNCHRONOUS CONDENSER:
An over-excited Synchronous Motor running at no load is known as Synchronous Condenser. A synchronous Motor takes a leading current when over-excited and behaves like a capacitor. It is connected in parallel with the equipment and it draws leading current which neutralises the lagging reactive component of the equipment. Thus Power Factor is improved.
ADVANTAGES:
- By varying the field excitation of the motor, magnitude of current drawn by the motor can be controlled. This helps in achieving smooth control of power factor
- Have longer life.
- Faults can be easily removed.
- Motor Windings have high thermal stability to short circuit currents.
DISADVANTAGES:
- There are significant losses in the motor.
- Maintenance Cost is high.
- It produces noise.
- Since, Synchronous Motor is not self Starting, therefore it requires auxiliary equipment to provide starting torque.