What is a Synchronous Machine?
Synchronous Machine constitutes of both synchronous motors as well as synchronous generators. An AC system has some advantages over a DC system. Therefore, the AC system is exclusively used for the generation, transmission, and distribution of electric power. The machine which converts mechanical power into AC electrical power is called a Synchronous Generator or Alternator. However, if the same machine can be operated as a motor is known as Synchronous Motor.
SYNCHRONOUS SPEED:
Synchronous machine is an AC machine whose satisfactory operation depends upon the maintenance of the following relationship.
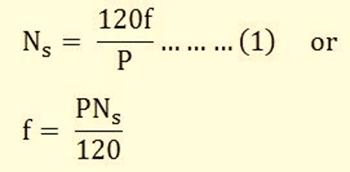
Where,
- Ns is the synchronous speed in revolution per minute (r.p.m)
- f is the supply frequency
- P is the number of poles of the machine.
ADVANTAGES OF ROTATING FIELD:
- Stationary Armature can be easily insulated for higher voltages.
- Since the armature windings are stationary, they are not subjected to vibrations and centrifugal forces.
- Output Current can be easily taken as terminals are fixed on the stationary armature. No need of using slip rings and brushes.
- Only 2 slip rings are required for providing direct current to the rotating field, while at least 3 slip rings would be required for the rotating armature ( that too of higher voltages).
- Size of the machine is reduced.
- Rotating field is comparatively light and can be constructed for high speed rotations.
- Cooling becomes more easier in the case of stationary armature.
Functionally, Synchronous Machine are of two types – Synchronous Motor and Synchronous Generator (Alternator).



